Science
| Subject Leader | Mrs S Cross |
| Contact Details | lowersite@brinkworthearldanbys.wilts.sch.uk for the attention of the Science Subject Leader |
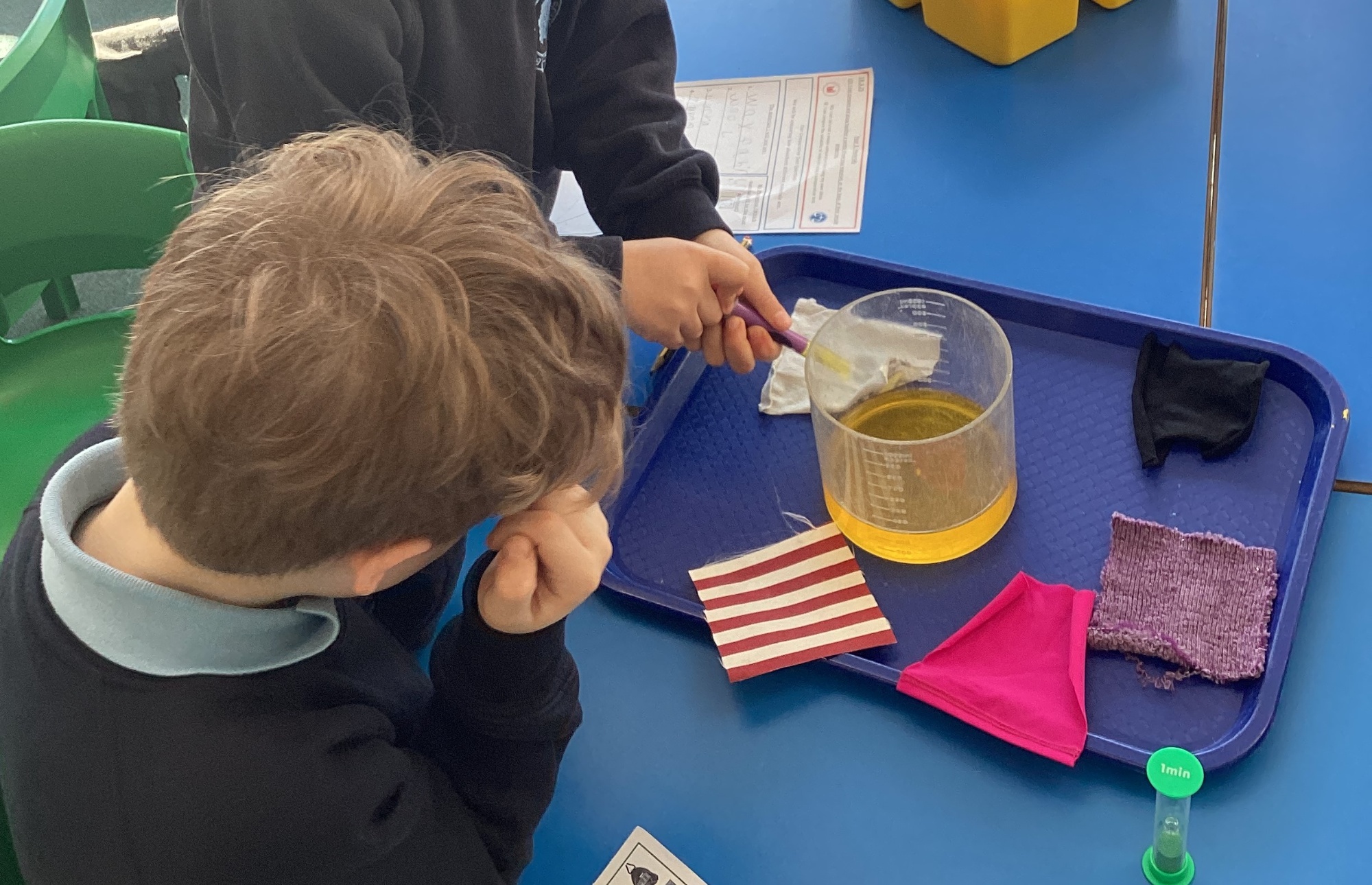
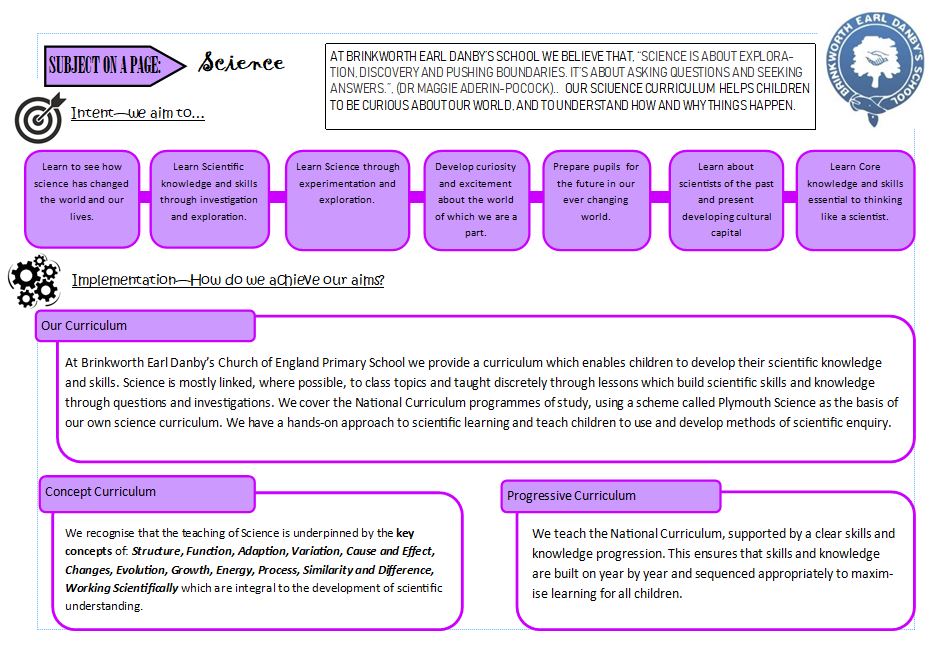
| Mission Sentence | At Brinkworth Earl Danby's School we believe that "Science is about exploration, discovery and pushing boundaries. It's about asking questions and seeking answers," (Dr Maggie Aderin-Pocock). Our science curriculum helps children to be curious about our world and to understand how and why things happen. |
| Inspiring Quotes |
|
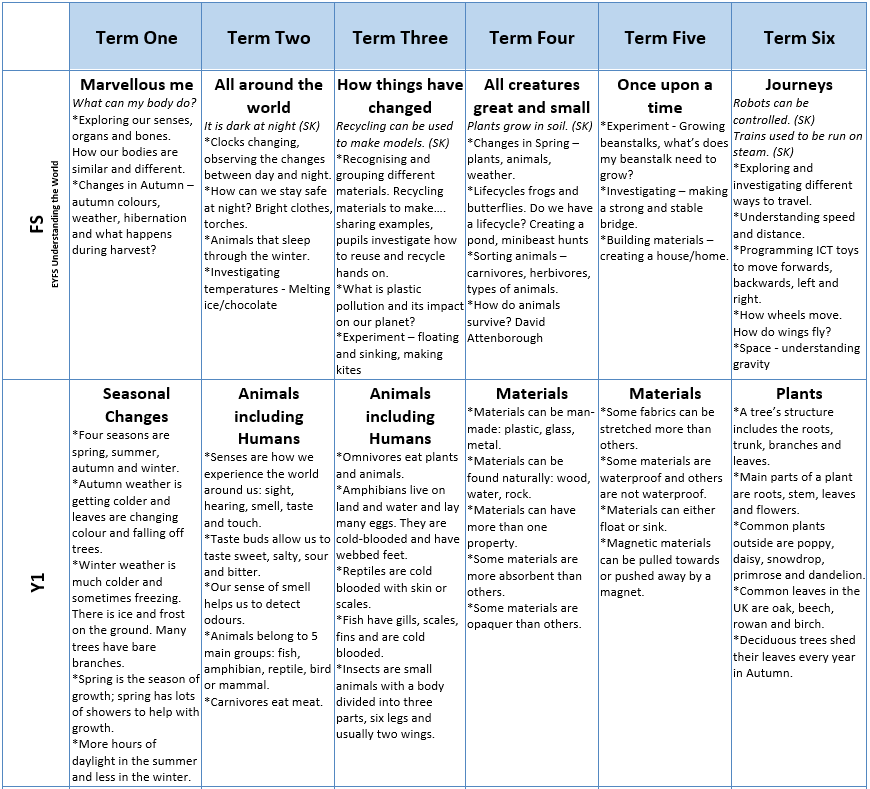
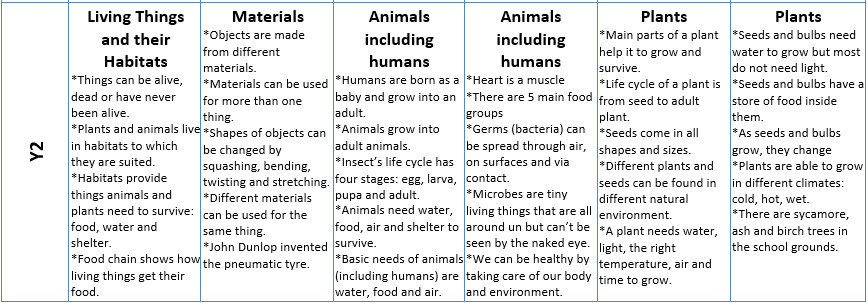
Curriculum Overview
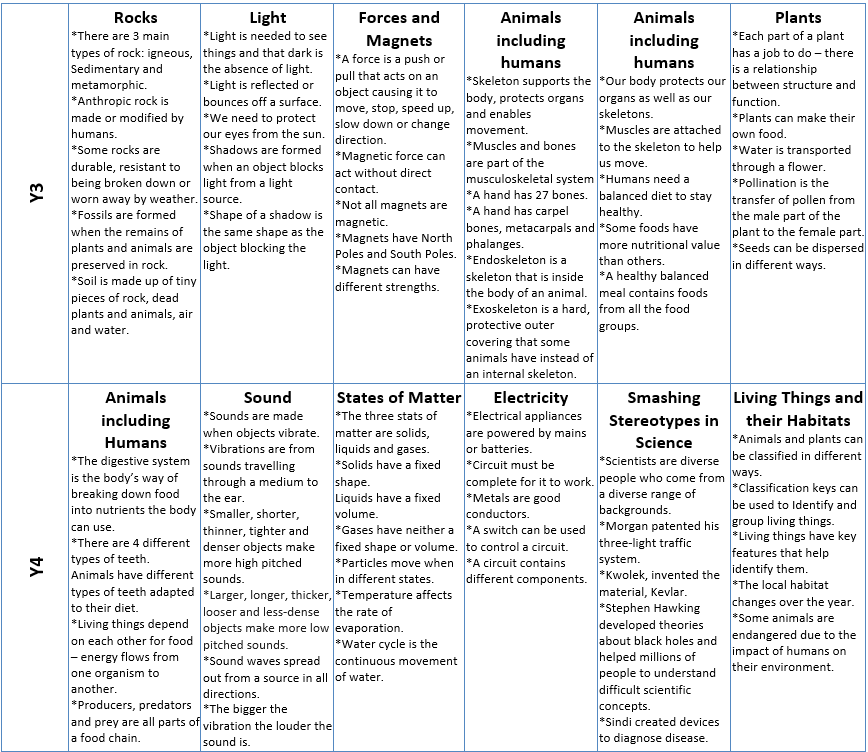
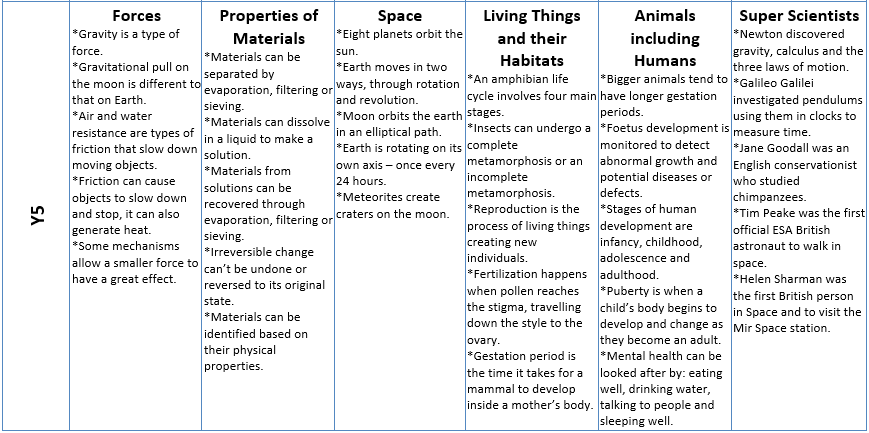
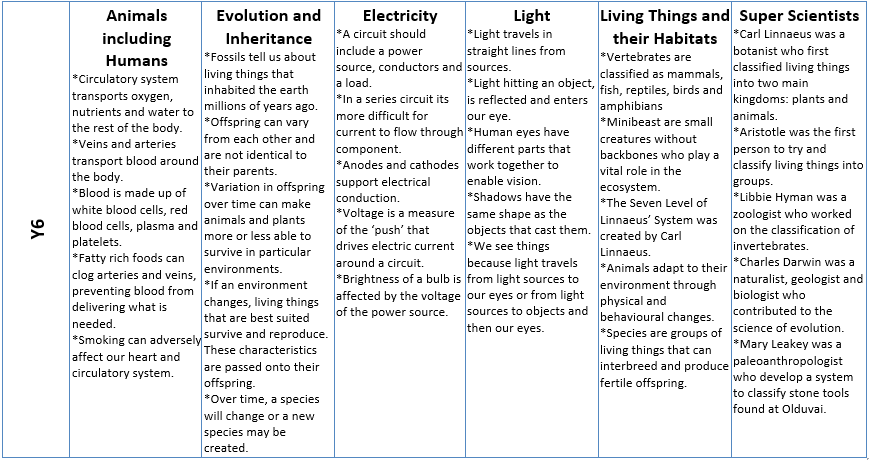
Some famous scientists we are inspired by...
Dr Maggie Aderin-Pocock (b. 1968)
Albert Einstein (1879 – 1955)
Thomas Edison (1847 – 1931)
Sally Ride (1951 – 2012)
Sir David Attenborough (b. 1926)
Marie Curie (1867 – 1934)